 |
| Brown dwarf in relation to Earth, Jupiter, a low-mass star and the sun. CREDIT: NASA |
A dark object may be lurking near our solar system, occasionally kicking comets in our direction.
Nicknamed “Nemesis” or “The Death Star,” this undetected object could be a red or brown dwarf star, or an even darker presence several times the mass of Jupiter.
Why do scientists think something could be hidden beyond the edge of our solar system? Originally, Nemesis was suggested as a way to explain a cycle of mass extinctions on Earth.
The paleontologists David Raup and Jack Sepkoski claim that, over the last 250 million years, life on Earth has faced extinction in a 26-million-year cycle. Astronomers proposed comet impacts as a possible cause for these catastrophes.
Our solar system is surrounded by a vast collection of icy bodies called the Oort Cloud. If our Sun were part of a binary system in which two gravitationally-bound stars orbit a common center of mass, this interaction could disturb the Oort Cloud on a periodic basis, sending comets whizzing towards us.
An asteroid impact is famously responsible for the extinction of the dinosaurs 65 million years ago, but large comet impacts may be equally deadly. A comet may have been the cause of the Tunguska event in Russia in 1908. That explosion had about a thousand times the power of the atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima, and it flattened an estimated 80 million trees over an 830 square mile area.
While there’s little doubt about the destructive power of cosmic impacts, there is no evidence that comets have periodically caused mass extinctions on our planet.
The theory of periodic extinctions itself is still debated, with many insisting that more proof is needed. Even if the scientific consensus is that extinction events don’t occur in a predictable cycle, there are now other reasons to suspect a dark companion to the Sun.
The Footprint of Nemesis
 |
| Comparing sizes. Credit: NASA |
"Sedna shouldn't be there,” said Brown. “There's no way to put Sedna where it is. It never comes close enough to be affected by the Sun, but it never goes far enough away from the Sun to be affected by other stars.”
Perhaps a massive unseen object is responsible for Sedna’s mystifying orbit, its gravitational influence keeping Sedna fixed in that far-distant portion of space.
“My surveys have always looked for objects closer and thus moving faster,” Brown told . “I would have easily overlooked something so distant and slow moving as Nemesis.”
John Matese, Emeritus Professor of Physics at the University of Louisiana at Lafayette, suspects Nemesis exists for another reason. The comets in the inner solar system seem to mostly come from the same region of the Oort Cloud, and Matese thinks the gravitational influence of a solar companion is disrupting that part of the cloud, scattering comets in its wake.
His calculations suggest Nemesis is between 3 to 5 times the mass of Jupiter, rather than the 13 Jupiter masses or greater that some scientists think is a necessary quality of a brown dwarf.
Even at this smaller mass, however, many astronomers would still classify it as a low mass star rather than a planet, since the circumstances of birth for stars and planets differ.
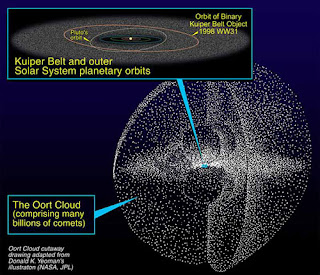 |
| Illustration of the “Oort Cloud,” a vast region of comets thought to extend a light year beyond our Sun. Image credit: NASA/JPL/Donald K. Yeoman |
The Oort Cloud is thought to extend about 1 light year from the Sun. Matese estimates Nemesis is 25,000 AU away (or about one-third of a light year). The next-closest known star to the Sun is Proxima Centauri, located 4.2 light years away.
Richard Muller of the University of California Berkeley first suggested the Nemesis theory, and even wrote a popular science book on the topic. He thinks Nemesis is a red dwarf star 1.5 light years away. Many scientists counter that such a wide orbit is inherently unstable and could not have lasted long – certainly not long enough to have caused the extinctions seen in Earth’s fossil record. But Muller says this instability has resulted in an orbit that has changed greatly over billions of years, and in the next billion years Nemesis will be thrown free of the solar system.
Binary star systems are common in the galaxy. It is estimated that one-third of the stars in the Milky Way are either binary or part of a multiple-star system.
Red dwarfs are also common – in fact, astronomers say they are the most common type of star in the galaxy. Brown dwarfs are also thought to be common, but there are only a few hundred known at this time because they are so difficult to see. Red and brown dwarfs are smaller and cooler than our Sun, and do not shine brightly. If red dwarfs can be compared to the red embers of a dying fire, then brown dwarfs would be the smoldering ash.
Because they are so dim, it is plausible that the Sun could have a secret companion even though we’ve searched the sky for many years with a variety of instruments.
Can Wise discover Nemesis?
WISE looked at our universe in the infrared part of the spectrum. Like the Spitzer space telescope, WISE is hunting for heat. The difference is that WISE has a much wider field of view, and so was able to scan a greater portion of the sky for distant objects.
Part of the WISE mission was to search for brown dwarfs, and NASA expects it could find one thousand of the dim stellar objects within 25 light years of our solar system. If Nemesis is there, WISE should have detected.
WISE scanned the sky twice in order to generate the time-lapsed images astronomers use to detect objects in the outer solar system.
It is too early to know whether WISE data confirms or rules out a large object like Nemesis. Analysis over the next couple of years will be needed to determine if WISE has actually detected such a object or not. The first 14 weeks of data, being released in April 2011, are unlikely to be sufficient.
The full survey, scheduled for release in March 2012, should provide greater insight.
Now comes the long task of analyzing the data.
source: Astrobiology Magazine
No comments:
Post a Comment